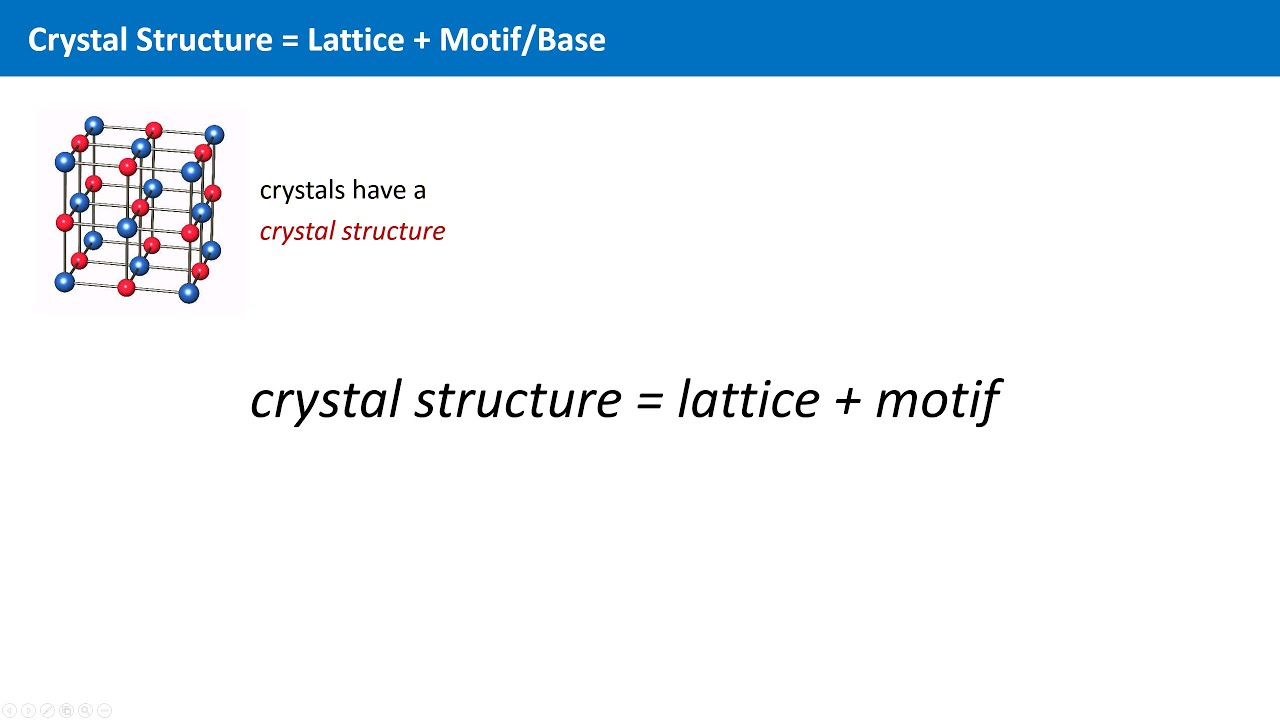
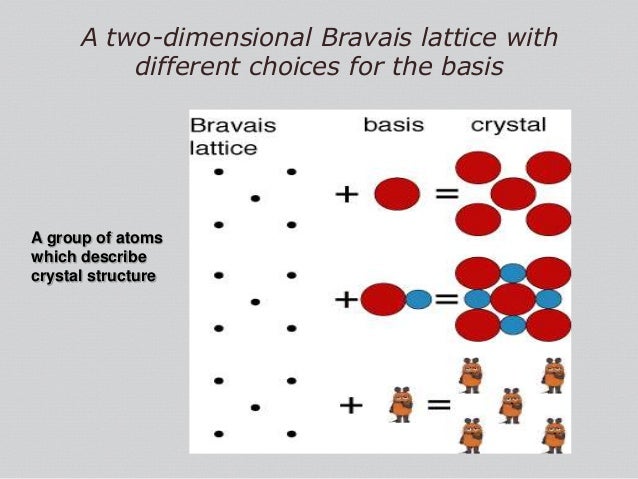
This generates a structure that is referred to as a crystal a crystalis defined as a latticewith a basisadded to each lattice site.
Describe this structure as a attice and a basis.
Thus in fig 2 the basis is represented by the two atoms a and a1.
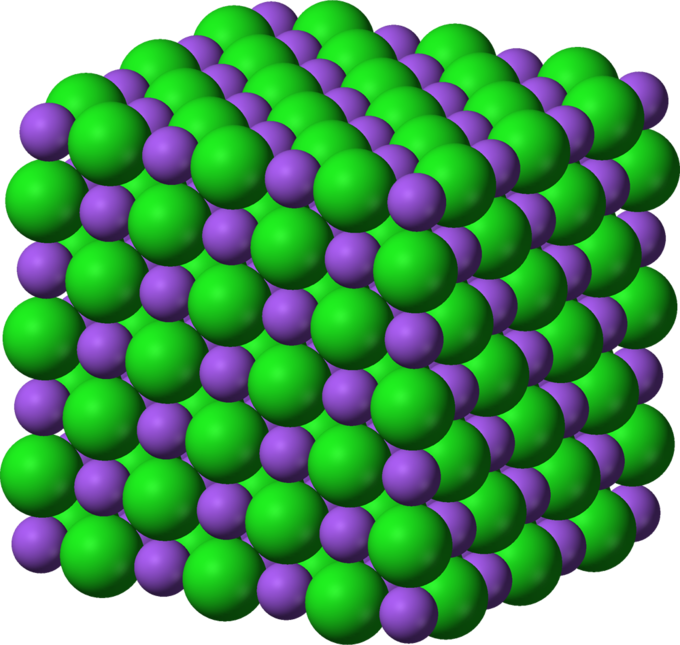
Crystal lattices can be classified as either monatomic or polyatomic.
Clearly it is not a bravais lattice in a bravais lattice the lattice must look exactly the same when viewed from any lattice point it can be thought of as a bravais lattice with a basis consisting of more than just one atom per lattice point two atoms in this case.
1 diamond structure fig.
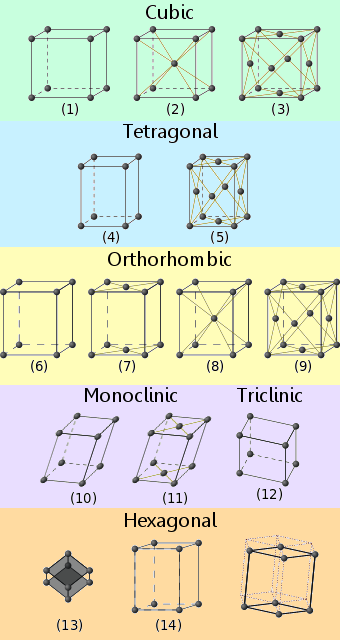
The lattice is defined by fundamental translation vectors.
In a general case crystal structure can be considered as crystal structure lattice basis.
Usually the basis consists of an atom a group of atoms or a molecule.
The basis is a set of atoms which is located near each site of a bravais lattice.
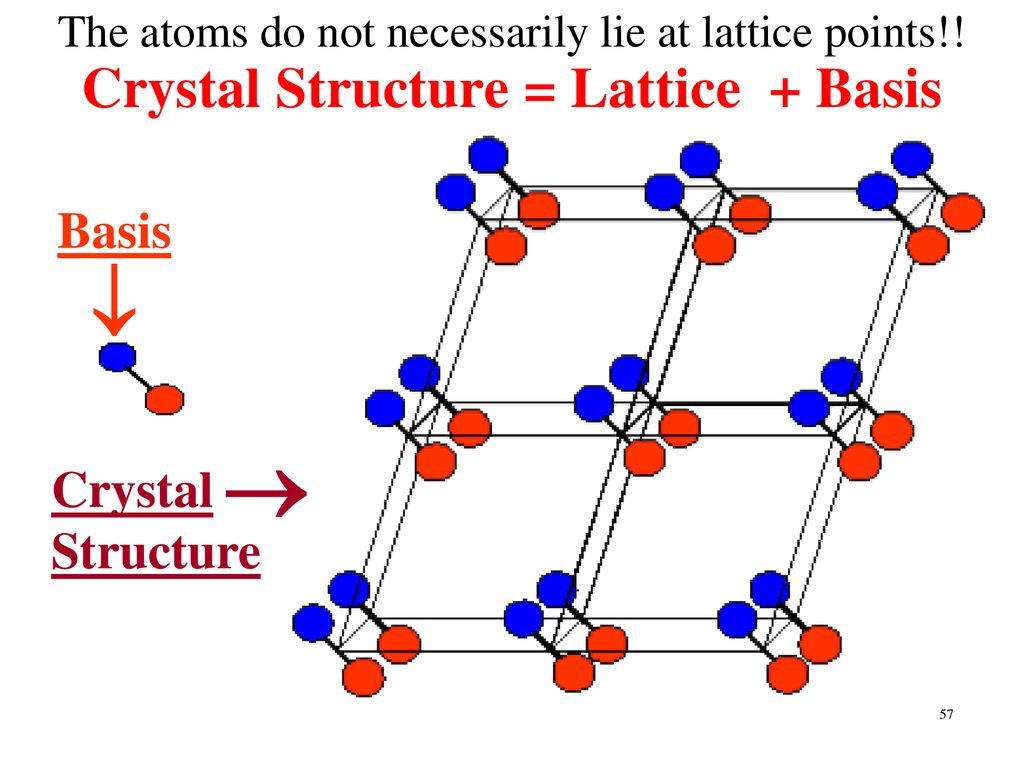
3 8 from kittel the crystal structure is formed by the addition of the basis b to the lattice points of the lattice a.
If there is only one type of.
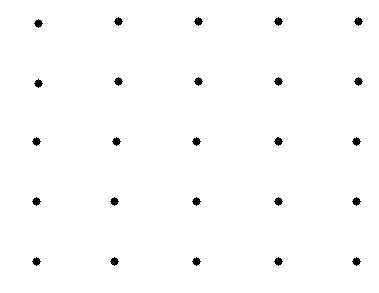
Lets see how a two dimensional lattice may look.
It does not matter where the basis is put in relation to a lattice point.
This classification is based on the kind of atoms present in the face within a lattice structure.
Conventional or prescriptive construction practices are based as much on experience as on technical analysis and theory.
It is used to describe the structure of a crystal.
A basis is a collection of atoms in particular fixed arrangement in space.
Lattice with a basis consider the following lattice.
An atom or a group of atoms associated with each lattice point in crystal.
Translationally periodic arrangement of points in space.
When incorporated into a building code prescriptive sometimes called cookbook construction requirements can be easily followed by a builder and inspected by a code official without the services of a design professional.